HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY (HTO)
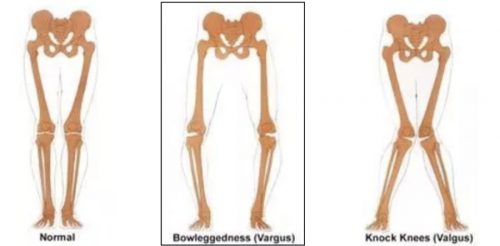
A high tibial osteotomy is a surgical procedure used to treat isolated medial compartment articular cartilage damage in patients who have varus malalignment (bow-legged).
WHO IS A CANDIDATE FOR A HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY?
High tibial osteotomies are used to treat patients who have only one area of damage within their joint and bow-legged malalignment. A high tibial osteotomy can be used alone as treatment for medial compartment osteoarthritis or to correct alignment in conjunction with a cartilage repair procedure. To determine if a high tibial osteotomy is an appropriate procedure for you, your surgeon will obtain a few different imaging studies. These studies will include regular x-rays, bone length x-rays (to determine your alignment), and possibly an MRI. Using these studies, your surgeon will be able to calculate the angle needed to correct your malalignment. High tibial osteotomies are commonly used to treat knee osteoarthritis of the medial compartment in active patients who are too young to have a joint replacement or whose activity level is such that they would damage or wear out an artificial joint prematurely. Our average patients who undergo high tibial osteotomies are ages 40-55 with isolated medial compartment osteoarthritis.
.
TIBIAL TUBERCLE OSTEOTOMY (TTO)
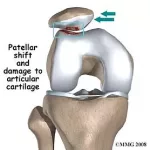
A Tibial Tubercle Osteotomy (TTO) is a surgical procedure used to treat patella (kneecap) maltracking with or without cartilage defects.
WHO IS A CANDIDATE FOR A TIBIAL TUBERCLE OSTEOTOMY?
Tibial tubercle osteotomies are used to treat patients who suffer from painful patellar maltracking. These patients may have had issues with patella dislocations in the past. Often, patients who suffer from patellar maltracking have chronic anterior knee pain. This is typically felt as pain with going up and down stairs and/or sitting for prolonged periods of time. Tibial tubercle osteotomies are only effective in patients who do not yet have bone on bone osteoarthritis between their patella and femur (patellofemoral joint). Tibial tubercle osteotomies can be performed in conjunction with MACI (matrix autologous chondrocyte implantation) as an effort to treat both the maltracking and the cartilage damage caused by it.
Read More – Tibial Tubercle Osteotomy
DISTAL FEMORAL OSTEOTOMY (DFO)
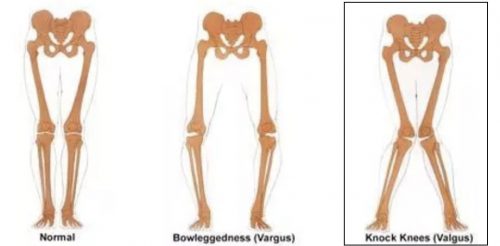
A distal femoral osteotomy is a surgical procedure used to treat isolated lateral compartment articular cartilage damage in patient who have valgus malalignment (knock-kneed).
WHO IS A CANDIDATE FOR A DISTAL FEMORAL OSTEOTOMY?
Distal femoral osteotomies are used to treat patients who have only one area of damage within their joint who are bow-legged. A distal femoral osteotomy can be used alone as treatment for lateral compartment osteoarthritis or to correct alignment in conjunction with a cartilage repair procedure. To determine if a distal femoral osteotomy is an appropriate procedure for you, your surgeon will obtain a few different imaging studies. These studies will include regular x-rays, bone length x-rays to determine your alignment, and possibly an MRI. Using these studies, your surgeon will be able to calculate the angle he will need to use in order to correct your malalignment.
Distal femoral osteotomies are most commonly used to treat arthritis in active patients who are too young to have a joint replacement or whose activity level is such that they would damage or wear out an artificial joint prematurely. Distal femoral osteotomies are also used in conjunction with MACI (matrix autologous chondrocyte implantation) for the management of isolated chondral defects in the lateral compartment in the setting of valgus malalignment.
Rehabilitation Protocols
Email Address
aitinger@paleyinstitute.org
Phone Number
561-844-5255
